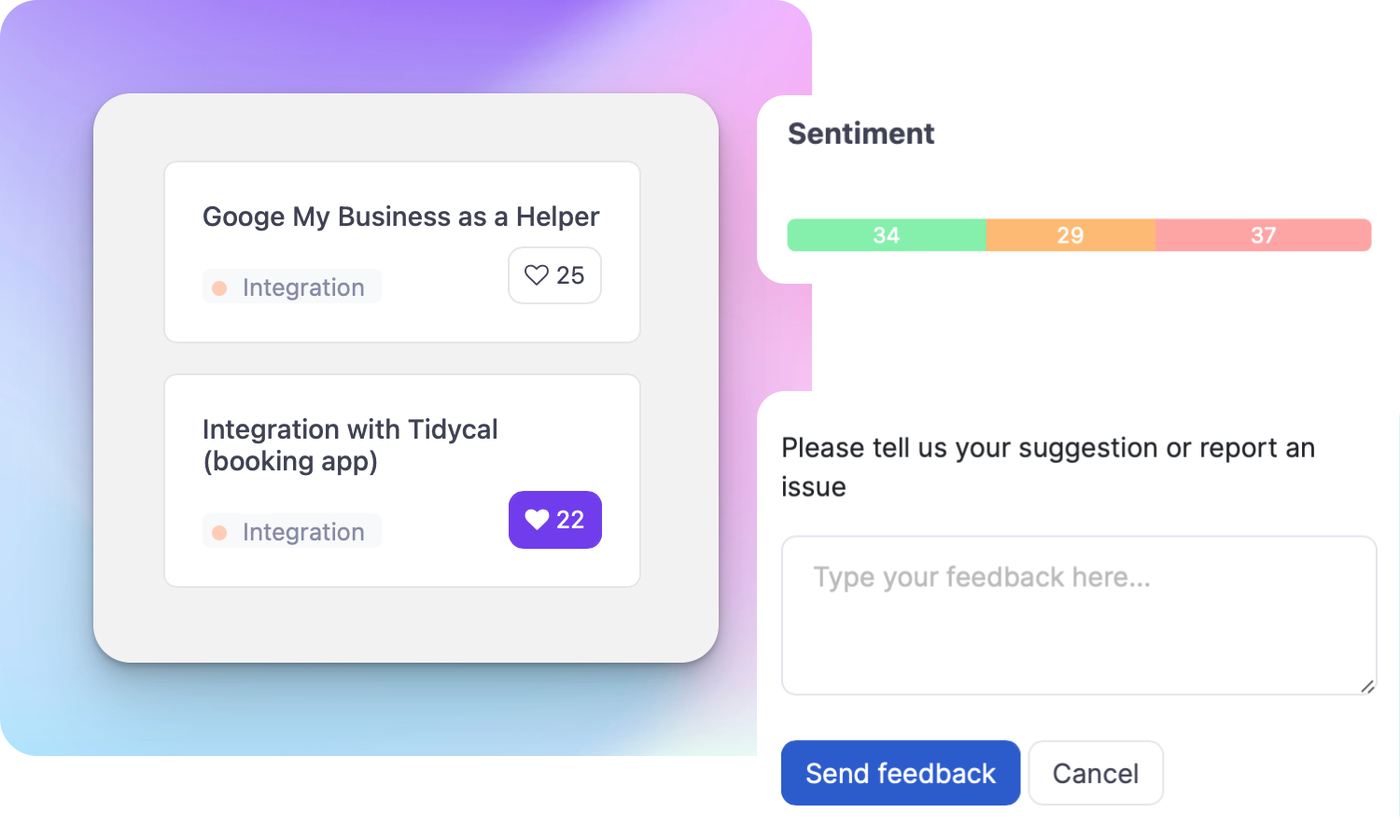
What is an User Interface?

Ruben Buijs
User Interface (UI) refers to the visual and interactive elements through which users interact with a product, system, or application. It encompasses everything that users see, hear, and interact with, including buttons, menus, forms, icons, and other graphical elements.
Examples
Some examples of user interfaces include:
- A mobile app with a clean and intuitive layout, allowing users to easily navigate and perform tasks.
- A website with a well-designed menu and search functionality, enabling users to find information quickly.
- A software application with clear and informative error messages, helping users understand and resolve issues.
Importance
A well-designed user interface is crucial for the success of a product as it directly impacts user satisfaction and engagement. Here's why user interface matters:
- Usability: A user-friendly interface enhances the overall usability of a product, making it easy for users to learn, navigate, and accomplish their goals efficiently.
- Engagement: An aesthetically pleasing and interactive interface can captivate users' attention, increasing their engagement and encouraging them to explore and interact with the product.
- Efficiency: An intuitive interface streamlines user workflows, allowing them to complete tasks quickly and with minimal effort.
- Brand Image: The user interface serves as the face of a product, reflecting its brand identity and values. A visually appealing and consistent interface can help establish a positive brand image.
How to Use User Interface
To create an effective user interface, consider the following guidelines:
- Understand your users: Conduct user research to understand your target audience's needs, preferences, and pain points. This insight will guide your interface design decisions.
- Keep it simple: Strive for simplicity and clarity in your interface design. Avoid cluttered layouts and unnecessary elements that may confuse or overwhelm users.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent visual style and interaction patterns throughout the interface. This helps users build familiarity and reduces cognitive load.
- Visual Hierarchy: Use visual cues such as color, size, and contrast to establish a clear hierarchy of information. This guides users' attention and helps them prioritize tasks.
- Responsive Design: Ensure your interface is responsive and adaptable to different devices and screen sizes. This provides a seamless user experience across various platforms.
- Feedback and Guidance: Provide timely and relevant feedback to users when they interact with the interface. Use descriptive labels, tooltips, and error messages to guide users and prevent errors.
Useful Tips
Here are some additional tips to enhance your user interface:
- Conduct usability testing to gather feedback from real users and identify areas for improvement.
- Stay updated with current design trends and best practices to create modern and visually appealing interfaces.
- Continuously iterate and refine your interface based on user feedback and evolving user needs.
- Collaborate closely with developers and other stakeholders to ensure the interface is technically feasible and aligns with the overall product vision.
Related Terms
- User Experience (UX)
- Information Architecture
- Interaction Design
- Wireframing
- Prototyping
- Responsive Design
- Accessibility
- Visual Design
- Microinteractions
- Gamification